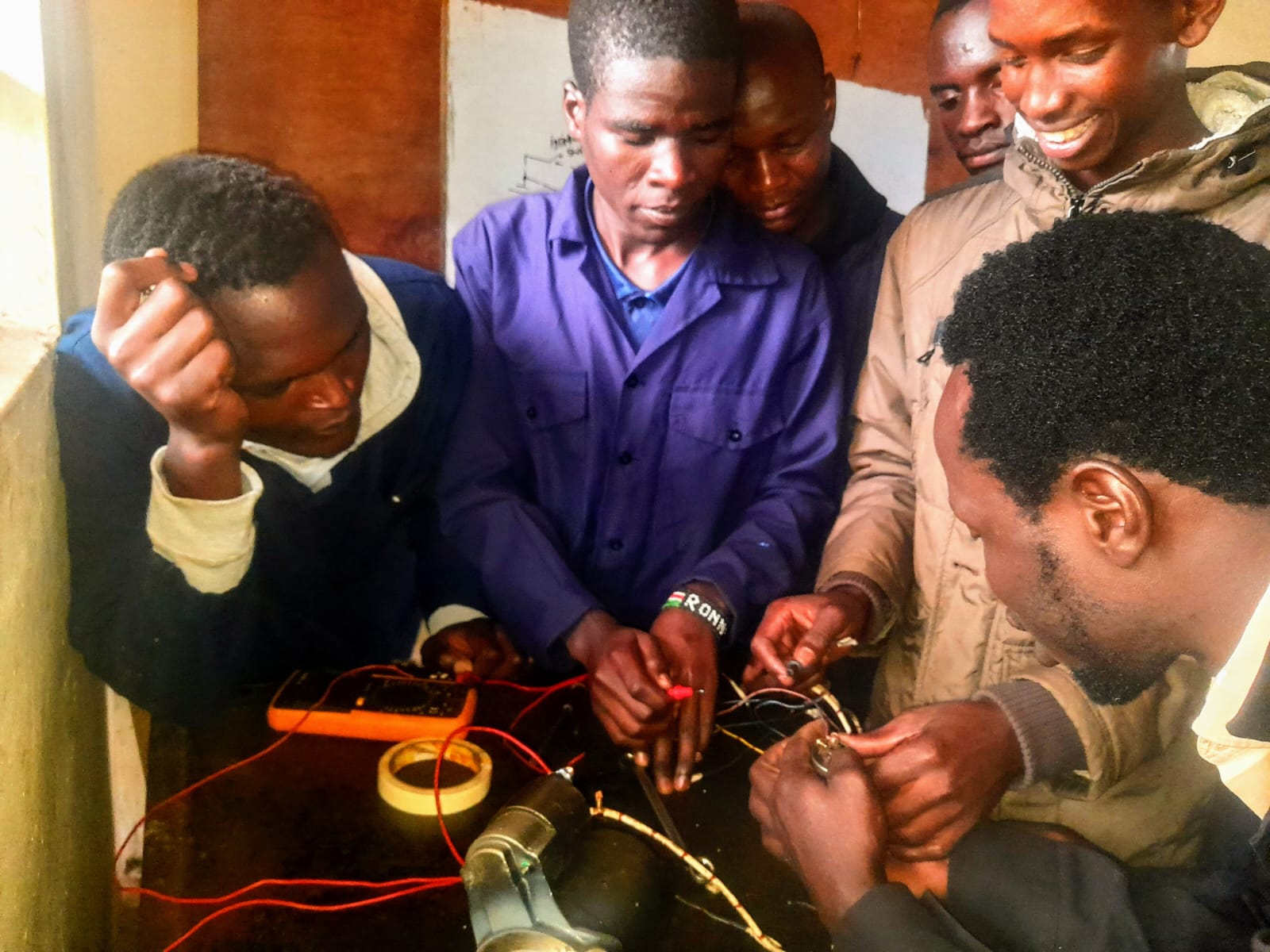
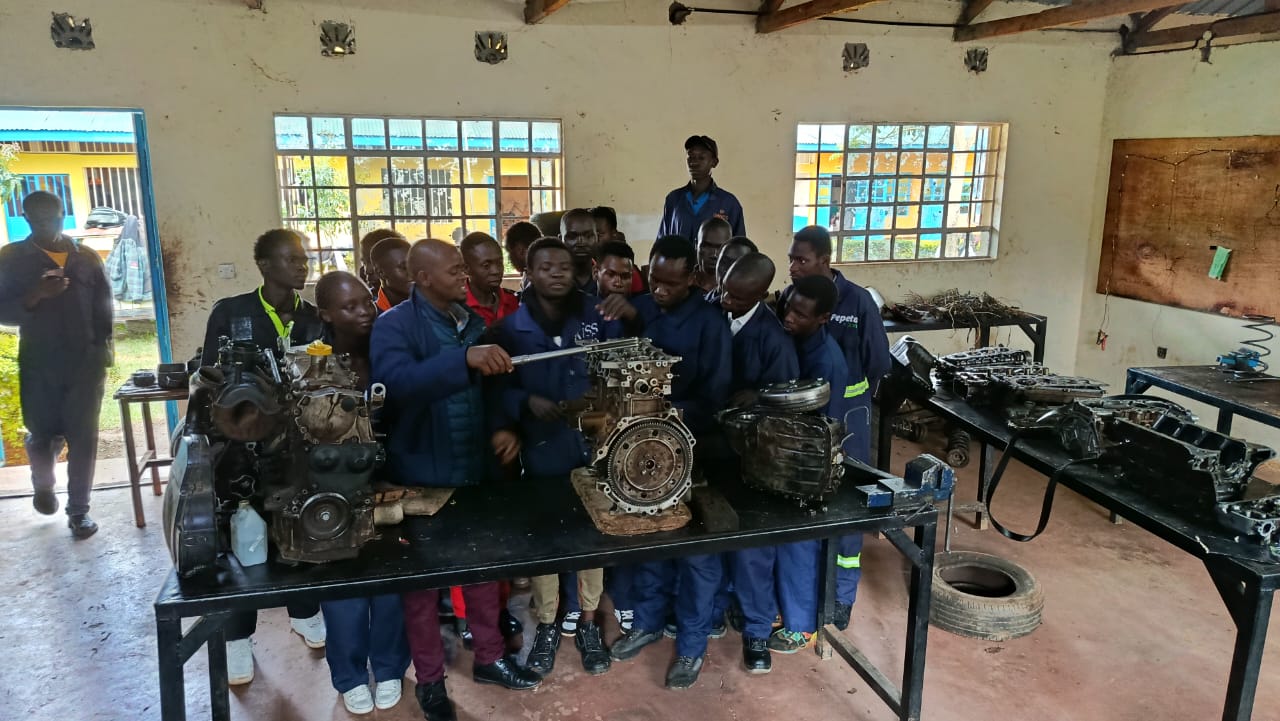
· Automotive Engineering is a branch of vehicle engineering that focuses on the design, development, manufacturing, and testing of vehicles and their systems. It combines elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software, and safety engineering to create innovative and efficient transportation solutions.
Key Areas of Automotive Engineering:
1. Vehicle Design and Development
· Styling and aesthetics
· Aerodynamics and ergonomics
· Structural design and materials
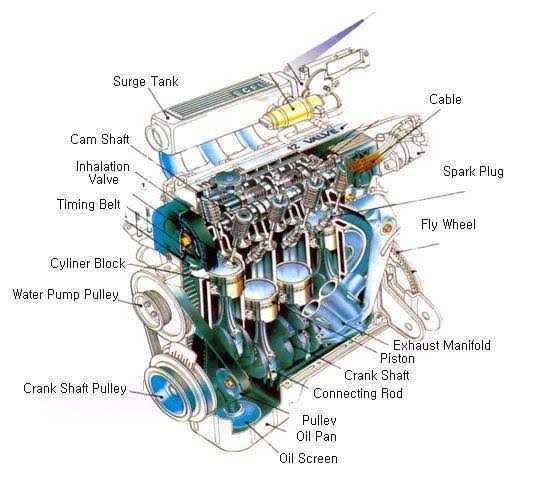
2. Powertrain Engineering
· Engine and transmission design (internal combustion or electric)
· Fuel efficiency and emissions control
· Hybrid and electric power systems
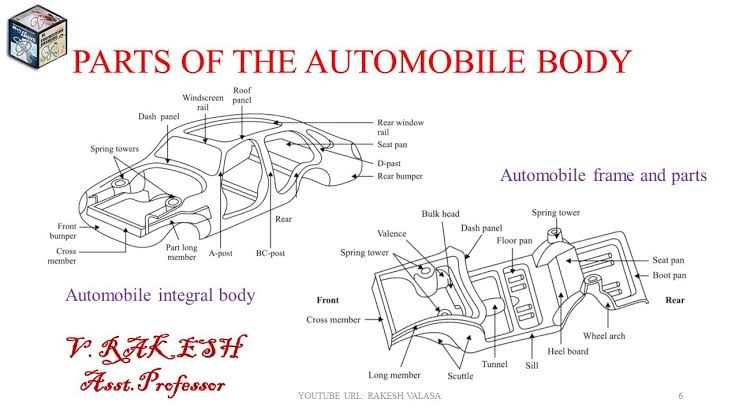
3. Chassis and Suspension Systems
· Frame design
· Brakes, steering, and suspension systems
· Ride quality and handling performance
4. Electrical and Electronic Systems
· Battery systems and energy management
· Sensors, ECUs (electronic control units), and infotainment
· Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving
5. Manufacturing and Production
· Assembly line automation
· Quality control and materials testing
· Cost efficiency and supply chain logistics
6. Safety and Environmental Considerations
· Crashworthiness and passive safety systems (airbags, crumple zones)
· Emission regulations and sustainability
· Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) control
Career Opportunities:
· Automotive Engineer
· Powertrain Specialist
· Vehicle Dynamics Engineer
· Safety Systems Engineer
· Embedded Systems Developer
· Electric Vehicle (EV) Engineer
Importance:
Automotive engineering plays a vital role in shaping the future of mobility, especially with the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, and sustainable transportation solutions.
Skip available courses
Available courses
AUTOCAD

AutoCAD is a computer-aided design (CAD) software application developed by Autodesk, widely used in architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing industries. It enables users to create precise 2D and 3D drawings and models for technical and engineering purposes. With a comprehensive set of tools for drafting, annotation, and design automation, AutoCAD helps professionals visualize concepts, simulate performance, and produce detailed plans and documentation. Its flexibility, accuracy, and compatibility with industry standards make it a leading choice for digital design and drafting.
· Teacher: Caleb tom
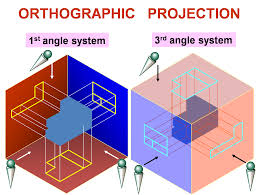
TECHNICAL DRAWING

Technical drawing, also known as drafting, is the process of creating precise and detailed representations of objects, structures, or systems using standardized symbols, dimensions, and notations. It is a critical tool in engineering, architecture, manufacturing, and design, used to convey information about the shape, size, materials, and assembly of a product or structure. Technical drawings can be done manually or with computer-aided design (CAD) software, and typically include orthographic views, isometric projections, sections, and detailed annotations to ensure accurate construction or production.